rhonda patrick on omega 3
Sources:
has shared insights about omega-3 fatty acids on various occasions. Here are some key takeaways from her discussions on the topic:
-
Omega-3 fatty acids, especially from fish, can reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. A study suggests they can lower the risk of dying from cardiovascular issues. Omega-3s are essential fatty acids 1.
-
There are three forms of omega-3: ALA (found in plants such as flaxseed and walnuts), EPA, and DHA (marine sources found in seafood). Not getting enough omega-3 from seafood was identified as one of the top six preventable causes of death, responsible for about 84,000 deaths per year 2.
-
Omega-3 supplementation has been shown to lower all-cause mortality, slow telomere attrition, delay brain aging, reduce inflammation, increase HDL, lower triglycerides, and improve cell membrane fluidity, which is essential for neurotransmitter function like norepinephrine, affecting focus and attention 3.
-
also discusses omega-3's anabolic potential, explaining how they may play a role in both preserving and supporting muscle mass, which could be significant for preventing disuse atrophy 4.
Please let me know if you would like more detailed information on any of these aspects of omega-3 fatty acids.
RELATED QUESTIONS-
What dose of omega-3s and type are important
Sources:
The dosage of omega-3 fatty acids important for health benefits varies depending on the individual and the desired health outcome. Here are insights from experts on dosing and types:
- For cardiovascular health, high doses of omega-3 fatty acids have shown benefits. A randomized controlled trial using a high dose of 4 grams of EPA and DHA per day found a greater reduction in cardiovascular events than a lower dose, suggesting that a certain threshold of fatty acids may be necessary for full benefit 1.
- Elevated triglycerides can be reduced significantly with omega-3 supplementation. Doses between two to four grams of EPA and DHA from fish oil were effective at lowering triglycerides by 20-40% 2 3.
- emphasizes that reaching a target blood level of omega-3, rather than just taking a supplement, is what counts. Therefore, dosing should be personalized and, if possible, guided by a blood test such as the omega-3 index to ensure efficacy 4.
- In the context of mental health, there is mention of a study where 9.6 grams of omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil per day over four months greatly reduced symptoms of bipolar depression. However, such high doses should be approached with caution and under medical supervision 5.
- discusses how omega-3 fatty acids can help preserve muscle mass with age and enhance athletic performance, with doses around 3 grams per day of EPA and DHA being beneficial 3 6.
These are general guidelines discussed by experts, but it's crucial to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized recommendations, especially when considering high doses or if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
Regarding the type of omega-3, EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), typically found in marine sources like fish oil, are frequently cited for their health benefits, particularly in reducing inflammation and improving cardiovascular health 4 2 1. ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), found in plant sources like flaxseeds, is a precursor to EPA and DHA but is not as bioavailable or directly linked to the benefits associated with EPA and DHA.
RELATED QUESTIONSHow can I monitor my omega-3 levels?
Sources:
To monitor your omega-3 levels, the most reliable and long-term biomarker is the Omega-3 Index, which measures the levels of omega-3s in red blood cell membranes. This method is preferred over measuring plasma phospholipids, which can reflect more recent dietary intake and not long-term status. Developed by Dr. Bill Harris and his colleagues, the Omega-3 Index is now used in numerous scientific studies and considered an important measure of omega-3 fatty acid status.
To properly measure your Omega-3 Index:
- Wait 120 days after altering omega-3 intake to account for red blood cell turnover before testing, ensuring an accurate reflection of your levels.
- Use a specialized lab test, such as those provided by OmegaQuant, which was co-founded by Dr. Harris.
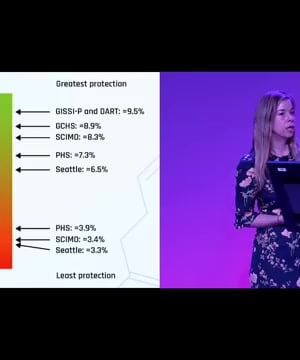
- Aim for an index of 8% or higher, which has been associated with a reduced risk of sudden cardiac death and improved cardiovascular health.
The typical American Omega-3 Index is around 4–5%, and achieving an 8–12% index is considered optimal for cardiovascular health, but reaching this range can be challenging and often requires increased intake of omega-3-rich foods or supplements 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8.
RELATED QUESTIONSdose of omega-3 for neurologic health
Sources:
A recommended dose of omega-3 fatty acids for neurological health, as discussed by , is around 2 grams (2000 milligrams) of omega-3 fatty acids per day in the form of EPA and DHA. This dosage is supported by various research studies. While some papers suggest higher amounts like 4 grams, these are said to be not an upper limit but rather the maximum dose a person could take considering cost and compliance. herself takes 4 grams per day, divided into 2 grams of EPA and 2 grams of DHA, in supplement form along with consuming fatty fish 1.
For those focused on cognitive function and seeking a cost-effective option, suggests that ingesting 1 to 3 grams of EPA can contribute to brain and body health, enhance focus, cognitive ability, and potentially reduce the amount of antidepressant medication necessary 2. Interestingly, highlights that approximately 8% of the brain's weight is omega-3, and evidence shows that optimal intake of omega-3 affects cognition and behavior. Furthermore, supplemental omega-3 increases nerve growth factor, which is crucial for brain development 3.
As dosage may vary from person to person depending on individual circumstances and different factors such as body weight, age, and dietary preferences, consultation with a healthcare provider is advisable before starting any supplementation regimen. Additionally, due to potential blood-thinning effects, it is especially important to consult a doctor before consuming high doses of fish oil 4.
RELATED QUESTIONS