Glucose Toxicity
Sources:
Glucose toxicity occurs when there's an excess of glucose in the bloodstream, leading to significant health implications. Trusted experts discuss various aspects of glucose toxicity and its impact on health.
-
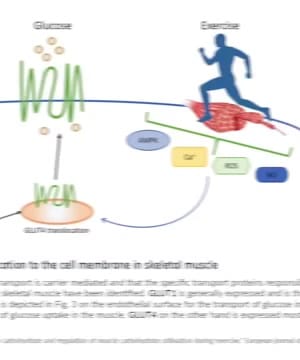
Chronic Glucose Toxicity: Elevated glucose levels can cause chronic toxicity, leading to complications in small blood vessels (eyes, kidneys, heart microvasculature, brain) and large blood vessels (aorta, iliac vessels, carotid arteries). This can significantly impact life expectancy. Elevated glucose makes proteins in blood sticky, occluding tiny capillaries and hampering oxygen delivery to tissues 1. Chronic high glucose can lead to various vascular diseases and is especially damaging to microvascular health 1.
-
Environmental Toxins and Glucose Levels: Exposure to environmental toxins like air pollution can increase blood glucose levels. Toxins disrupt the endocrine system and damage the beta cells of the pancreas, reducing insulin production and function, mimicking insulin resistance, which raises glucose levels 2.
-
Acute and Chronic Toxicity: While acute glucose toxicity (like a sudden surge to around 40 teaspoons of glucose) can lead to immediate health crises, chronic toxicity from moderate but persistently high levels causes systemic damage over time. This is often evident through conditions like diabetes, where excessive glucose demands disposal within short periods, unlike fats 3.
-
Glucose Impact on Brain Health: High glucose levels in the brain cause significant damage, killing brain cells and contributing to conditions like Alzheimer's, stroke, and other neurological issues. This is partly due to the lack of insulation from blood glucose for brain cells, leading to direct exposure and damage from elevated glucose 4.
-
Metabolic Implications: Glucose's role in protein glycosylation makes proteins stickier and less functional, leading to occlusion in small vascular systems. This begins a cascade of complications linked with insulin resistance and elevated insulin levels in attempts to manage high blood sugar 1.
These insights underline the importance of maintaining regulated blood glucose levels to avoid acute and chronic complications and the significant impacts of environmental and dietary factors on glucose metabolism.
RELATED QUESTIONS-