Why is exercise important?
Sources:
Exercise is crucial for numerous reasons, touching both physical and mental health.
Physical Benefits
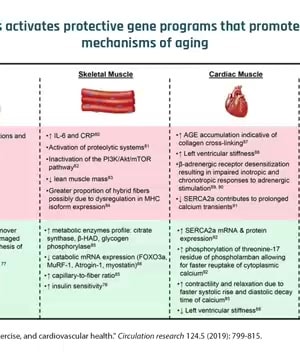
- Cellular and Mitochondrial Health: Exercise enhances the ability of muscle cells to clear out damaged proteins and dysfunctional organelles like mitochondria, promoting better energy production and cell function 1.
- Cancer Prevention: Regular aerobic exercise can reduce the risk of breast and colorectal cancers by producing myokines, anti-inflammatory effects, and improving insulin sensitivity. These mechanisms also help kill cancer cells and reduce cancer recurrence and metastasis 2.
- Metabolic Health: Short bursts of intense exercise, or "exercise snacks," improve blood glucose levels and insulin sensitivity, especially when done around meals. This helps manage conditions like type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome 3.
Mental Benefits
- Mood and Depression: Exercise increases endocannabinoids and beta-endorphins, which can elevate mood and reduce depressive symptoms. Vigorous aerobic exercise has been shown to help prevent and treat depression 4.
- Mental Clarity and Stress Handling: Physical activity improves mental clarity and reduces anxiety by enhancing executive function and decreasing activity in the brain's emotional centers, such as the amygdala 5 6.
- Brain Health: Regular exercise can stimulate mitochondrial biogenesis in brain cells, potentially enhancing cognitive functions and protecting against aging-related decline in brain health 1.
Practical Implementation
Incorporating exercise into daily life doesn't require extensive workouts. Short exercise intervals can be effective in breaking up sedentary periods, improving both mental and physical health markers.
Whether it's through structured workouts or brief exercise snacks, the insights from these studies emphasize the comprehensive benefits of staying physically active.
RELATED QUESTIONS