Election Surveys
Sources:
1. Advantages of Online Polling
In a discussion on the , , co-founder of Evite and tech executive, spoke about the transition of SurveyMonkey into the polling sector. SurveyMonkey managed to correctly predict the UK election by utilizing its large sample size from online panels instead of traditional phone calls. This method, partnered with NBC, proved effective in increasing brand awareness and displaying the accuracy of data collection through online surveys.1
2. Pitfalls of Early Polls
Mike Podhorzer, a political strategist, discussed on why panic over early polls, like the one showing Trump leading Biden in key swing states, is misjudged (2023). He argued that such polls do not accurately predict election outcomes and emphasized the difference between expressing opinions in polls and actual voting behavior.2
3. Validity of Polling Data
Professor Jo Hardin explained on the statistical perspective on election polls. She noted that while variations are expected due to sampling variability, consistent patterns, such as Clinton leading Trump, still emerge. This consistency adds credibility to data predictions within expected variability ranges.3
4. Challenges with Political Ads and Polls
Eric Zeng, an online ads researcher, revealed on how deceptive political ads can disguise themselves as polls. These ads aim to collect email addresses under the guise of gathering public opinion, often misleading users about the nature of the data collection and the use of their information.4
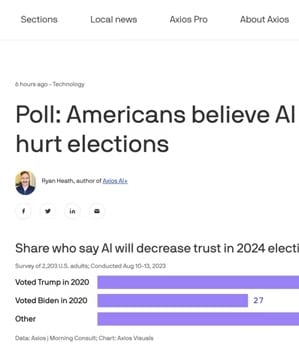
5. AI's Impact on Election Trust
Nathaniel Whittemore discussed a poll on about Americans' concerns over AI in elections. The poll indicated that around half of the respondents expected AI-driven misinformation to influence election outcomes. Furthermore, about one-third expressed reduced trust in election results due to AI's involvement, reflecting significant public skepticism towards AI's role in politics.5
Each of these aspects of election surveys provides insights into the evolving methodologies, challenges, and public perceptions surrounding electoral polling and predictions.
RELATED QUESTIONS