Glucose levels
Sources:
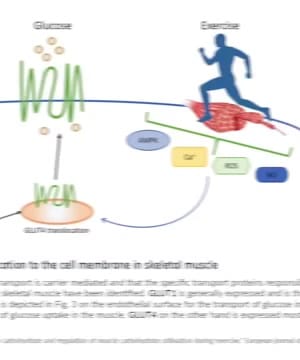
Elevated glucose levels have a chronic toxic effect that can lower life expectancy, and promote vascular issues, especially in the small blood vessels of critical areas like the eyes, kidneys, and the heart. Chronic high glucose levels make blood proteins stickier, which decreases their function and contributes to vascular occlusions. This can cause serious complications, particularly for those with conditions like type 2 diabetes 1.
Moreover, chronic high glucose levels usually precede high insulin levels, a condition known as hyperinsulinemia. This occurs when cells in the body become resistant to insulin, leading to an increase in glucose and insulin levels. Early detection of diabetes can often be done through eye examinations, revealing damages in the retina's capillaries 1.
In terms of dietary control, continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) is highly useful. It provides real-time data on how different foods affect blood glucose levels. For example, foods thought to be healthy might still cause unexpected glucose spikes if they contain hidden sugars 2.
For better glucose management, especially in individuals exploring diets like the ketogenic diet, knowing which foods trigger glucose spikes can be beneficial. Lifestyle factors, including sleep patterns, can also significantly impact glucose levels 3 2.
RELATED QUESTIONS