How does DNA methylation affect aging?
Sources:
DNA methylation impacts aging by altering the epigenetic landscape of cells, which can lead to changes in gene expression and cellular function over time. Here are some key points:
-
Epigenetic Clocks: Epigenetic aging clocks are tools that use DNA methylation patterns to estimate biological age. These clocks assess the methylation of CpG sites—regions where a cytosine nucleotide is followed by a guanine nucleotide—and help determine how closely a person's biological age aligns with their chronological age 1 2.
-
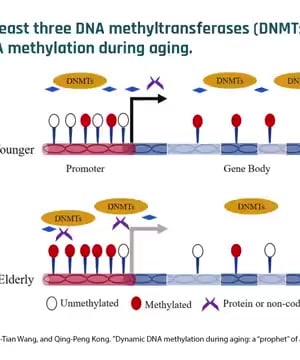
Cellular Aging: With aging, DNA methylation patterns become dysregulated. Normally methylated regions may lose methylation, and regions that shouldn’t have methylation may gain it. This dysregulation can repress or activate genes inappropriately, potentially leading to cellular malfunction and aging 1.
-
Disease Correlation: Changes in DNA methylation are also related to various diseases. For example, accelerated epigenetic aging in blood has been linked to Parkinson's disease, while Alzheimer's disease shows aging acceleration in brain tissue. Cancer tissues often exhibit significantly accelerated epigenetic aging compared to healthy tissue 3.
-
Stability and Mechanisms: Methylation patterns are stable and more consistent than other genomic measurements. They are influenced by genetic and environmental factors, and researchers are exploring how chronic signals like inflammation may drive changes in these patterns through enzymes such as DNA methyltransferases and demethylases 4 5.
-
Impact on Healthspan: The disarrangement of methylation patterns with age has significant biological implications. For instance, regions that should suppress tumor growth may become unmethylated, leading to cancer, or areas critical for cell repair may become over-methylated, impairing cellular maintenance and contributing to aging symptoms 6 7.
By understanding these mechanisms, researchers hope to develop interventions that can modify epigenetic clocks, potentially decelerating the aging process and mitigating age-related diseases.
RELATED QUESTIONS-